Differences in Brain Activity Across DISC Personality Types
- partedu
- Jul 22
- 3 min read

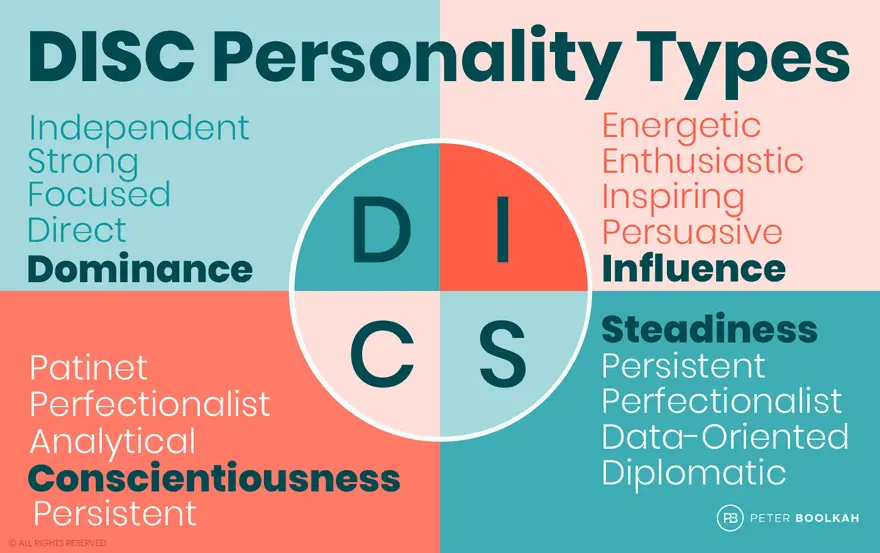
The DISC model consists of four primary behavioral patterns:
D: Dominance
I: Influence
S: Steadiness
C: Conscientiousness
D Type (Dominant): Quick Decision-Maker, Action-Oriented
Brain Activity:People with a dominant style tend to activate specific areas of the brain, particularly the left prefrontal cortex, which is associated with fast decision-making, risk-taking, and goal-oriented behavior. This brain region enables them to respond rapidly to situations and make effective decisions, often under pressure or uncertainty.
Perception & Intelligence:These individuals naturally make decisions faster than others, allowing quick action in critical situations. However, this speed may come at the cost of overlooking important details. Their focus on results can lead to missed key factors, which may impact the quality of their decisions.
Cognitive Focus:Their thinking revolves around the question: "How can I win?" This focus drives them to seek strategies and actions that lead to success, often making them effective in leadership and management roles. Their drive for achievement and performance often positions them as dynamic forces in teams and organizations.
I Type (Influential): Social, Inspirational
Brain Activity:High activity in the limbic system, especially the amygdala and reward centers, is common. These areas relate to emotions, social interaction, and positive reinforcement. The amygdala helps process emotional and social stimuli quickly, while the reward system encourages positive and engaging social behavior.
Perception & Intelligence:I types are highly responsive to others’ emotions and can quickly pick up on non-verbal cues like body language and tone. However, they may sometimes prioritize emotional intuition over deep logical analysis, which could limit their understanding of complex issues.
Cognitive Focus:They tend to ask: "Who can I attract?" Their orientation is toward building positive relationships, expanding social networks, and influencing others. Their ability to inspire and connect often places them as natural leaders in social environments.
S Type (Steady): Patient, Listener, Empathetic
Brain Activity:Increased activity in the medial prefrontal cortex and areas related to empathy and body language interpretation. These brain areas help individuals understand others’ emotions and respond appropriately, fostering strong and meaningful relationships.
Perception & Intelligence:They excel at understanding emotions and maintaining group harmony but may hesitate when quick decisions are needed. Their concern for others’ reactions can delay choices, making rapid decision-making challenging in high-pressure environments.
Cognitive Focus:Their main question is: "How can I create harmony?" They naturally aim to create balance and collaboration rather than competition, making them valuable as mediators or team facilitators.
C Type (Conscientious): Analytical, Precise, Task-Focused
Brain Activity:Significant activation occurs in regions responsible for data analysis, logical thinking, and error monitoring—especially the posterior prefrontal cortex. These areas are essential for processing complex information, critical thinking, and minimizing mistakes.
Perception & Intelligence:C types excel in problem-solving and critical analysis but may struggle in fast-paced social situations. Their deep focus on logic and detail can slow down their responsiveness in emotionally driven or informal settings.
Cognitive Focus:They focus on the question: "Is this correct and accurate?" These individuals value precision, rely on evidence, and tend to be skeptical of unverified claims. They thrive in scientific, research, and analytical environments.
Neuroscientific Perspective
Each DISC type reflects distinct cognitive and emotional brain patterns:
The left prefrontal cortex, prominent in D types, is critical for fast, goal-driven decisions but may lead to impatience or oversight.
The limbic system, dominant in I types, enhances emotional intelligence and social connection, but may affect rational objectivity.
Empathy-related regions like the medial prefrontal cortex are central in S types, promoting social harmony but sometimes delaying action.
Analytical zones in the posterior cortex, strong in C types, support precision and accuracy, though possibly at the cost of emotional responsiveness.
Understanding these neurological patterns can help individuals recognize their cognitive strengths and limitations, improve decision-making, and foster better interpersonal relationships.




Comments