The Impact of Parents’ DISC Behavioral Styles on Children’s Self-Confidence
- partedu
- Oct 20
- 11 min read

Parental behavior is one of the key factors in shaping children’s self-confidence. The DISC behavioral model, which introduces four behavioral styles, provides a useful framework for understanding parent–child interaction. This article examines the relationship between parents’ DISC behavioral styles and their children’s level of self-confidence, showing how each style can positively or negatively influence a child’s sense of self-worth. Finally, it offers practical recommendations for parents to help strengthen their children’s self-confidence.
Self-confidence, or self-efficacy, in children refers to an individual’s ability to believe in their own capabilities to face challenges. Parents, as the most important role models and reference points in a child’s developmental environment, play a crucial role in shaping this trait.
The DISC model, first introduced by William Moulton Marston in his book “Emotions of Normal People,” identifies four distinct behavioral styles and has been widely applied in educational, managerial, and family contexts.
The central question of this article is: “How do parents’ behavioral styles within the DISC model framework influence their children’s self-confidence?”
This question explores the deep and complex effects that different parenting approaches can have on the formation and development of children’s self-confidence.
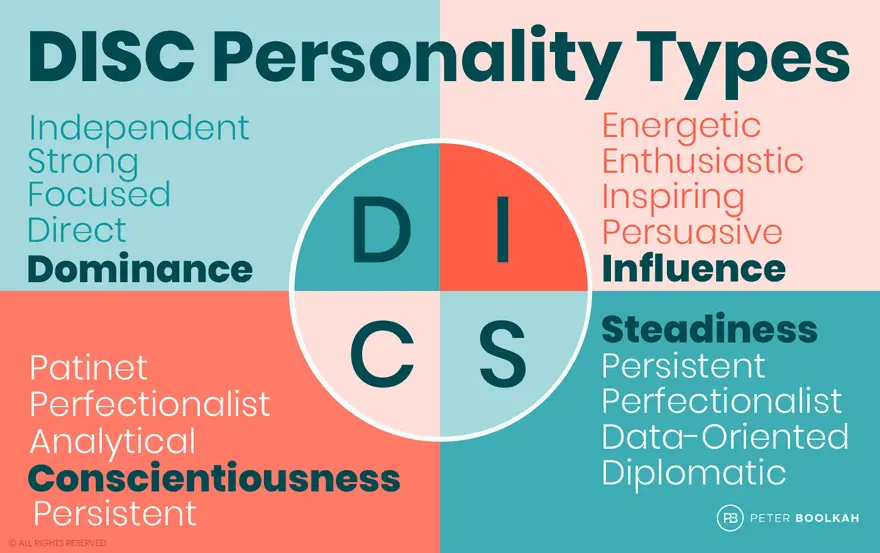
In this regard, the DISC model—which examines four primary behavioral styles—can serve as an effective tool for analyzing and better understanding these influences. These four styles include Dominance, Influence, Steadiness, and Conscientiousness, each with its own unique characteristics and behaviors.
For example, parents with a Dominant style often emphasize control and direction in raising their children and may consistently hold high expectations of them. Such behavior can help foster confidence in children but may also create psychological pressure and stress.
In contrast, parents who adopt an Influential style tend to focus more on encouragement and emotional support, which can enhance their children’s sense of self-worth and confidence.
Considering these factors, addressing this question can offer practical strategies for parents to promote the healthy and positive growth of their children’s self-confidence. These strategies may include educating parents on effective parenting methods, encouraging open and healthy communication with their children, and creating a positive and supportive environment for their development and flourishing.
Ultimately, by gaining a clearer understanding of how behavioral styles affect children’s self-confidence, parents can make more informed decisions in raising their children and contribute to improving their overall quality of life.
The DISC model is a tool for understanding individuals’ behavioral and communication styles. Research shows that this model can help parents become more aware of their own behaviors and use their personality strengths more constructively in interactions with their children.
Furthermore, studies on the development of a positive self-image in children indicate that this self-image is largely shaped by the reflection of parental behavior.
In other words:
A positive self-image forms the foundation for high self-confidence and self-esteem. This self-image not only affects how we interact with others but also plays a key role in our decision-making and life choices. We develop this image through the feedback and reactions of those around us, especially parents, teachers, and close friends. During the formative years of personality development, parents have the greatest influence. Through their words and actions, they teach us how to view ourselves and how to trust in our abilities and strengths.
For example, when parents recognize and encourage our achievements and efforts, this support can help build a positive self-image. Conversely, constant criticism and a lack of attention to accomplishments can lead to feelings of insecurity and self-doubt.
Beyond parents, the social and cultural environment in which we grow up also greatly affects our self-image. Society, media, and social role models can either support or undermine the formation of our self-perceptions. Therefore, it is important to be in environments that are supportive and positive, allowing us to express ourselves in the best possible way.
Ultimately, a positive self-image not only helps us resist challenges and hardships but also motivates us to pursue our goals and progress in life. It reminds us that we are valuable and capable of achieving what we desire. Hence, developing and maintaining a positive self-image is an ongoing process that requires attention and care.
Although direct research on the precise relationship between parents’ DISC indicators and children’s self-confidence is still limited, combining the concepts of the DISC model with child development psychology theories can provide a theoretical and analytical framework for examining these effects.
This article is written as a theoretical review and analyzes the topic by integrating the foundations of the DISC model, theories of children’s self-confidence development, and parental behavioral patterns.
The steps of the analysis are as follows:
1. Explaining each of the parents’ behavioral styles based on the DISC model.
2. Examining the potential effects of each style on children’s self-confidence.
3. Providing corrective and supportive strategies tailored to each style.
1. D Style (Dominant)
Parents with a D style are typically directive, decisive, and results-oriented. They expect their children to be goal-driven and successful, and as a result, they usually set high standards for their child’s performance. These parents aim for their children to achieve significant successes in academics, sports, and other areas.
The characteristics of this parenting style can be motivating, encouraging the child to strive harder, as the child may use these expectations as a stimulus to reach their goals. However, if this decisiveness and directive approach is not accompanied by emotional support and deep understanding, it may have negative consequences for the child.
For example, the child may feel that they are only valuable if they succeed and meet the goals set by their parents. Over time, this can create psychological pressure, where the child constantly seeks parental approval and validation. Consequently, when faced with failure or setbacks, the child’s self-confidence may significantly decline, and they may feel incapable of meeting parental expectations.
This situation can lead to anxiety and stress, preventing the child from engaging in new experiences and healthy challenges. Therefore, it is important for D-style parents not only to focus on outcomes and achievements but also to provide emotional support and understand their child’s emotional needs. Doing so can help strengthen the child’s self-confidence and create a healthy and positive environment for their growth.
2. I Style (Influential)
Parents with an I style are typically cheerful, social, and encouraging. They consistently strive to create a positive and supportive environment that enhances their children’s sense of security and well-being. This parenting approach makes the child feel loved and valued, which is a fundamental basis for healthy self-confidence.
I-style parents usually pay special attention to their children in daily activities, from play and recreation to deep and meaningful conversations, helping them develop their social and emotional skills. However, if parents place excessive emphasis on social approval and external validation, the child may learn to assess their self-worth based on others’ opinions and become dependent on external approval.
Over time, this dependency can lead to challenges in the child’s self-esteem and personal independence. For example, if a child is constantly seeking others’ approval, they may struggle with decision-making and find it difficult to distance themselves from others’ expectations and opinions. This can negatively affect their social relationships and cause stress and anxiety in various situations.
Therefore, parents need to balance encouragement with fostering independence, enabling their children not only to benefit from emotional support but also to develop the ability to evaluate and recognize their own intrinsic values.
3. S Style (Steady)
Parents with an S style provide a calm, safe, and predictable environment for their children, specifically designed to meet their emotional and psychological needs. This environment not only ensures physical safety but also fosters an emotional space where the child feels comfortable and at ease.
Providing such a setting allows the child to express their feelings freely, leading to a better understanding of themselves and the world around them. In this environment, the child can make mistakes without fear of judgment or punishment. These experiences enable them to learn from their errors and gradually strengthen their problem-solving and critical thinking skills.
In fact, this type of parenting teaches the child that failures and minor mistakes are part of the learning process, not signs of incapability or deficiency. The genuine and lasting self-confidence developed in such an environment helps the child feel empowered and capable when facing challenges and new situations. This self-confidence not only benefits them during childhood but continues to have positive effects into adulthood.
S-style parenting usually has the most positive impact on children’s self-confidence because it emphasizes unconditional acceptance and emotional support. By showing unconditional love and support, parents convey to the child that they are valuable and loved for who they are. This type of acceptance helps the child embrace themselves and trust in their own abilities, which in turn strengthens their social and communication skills. Ultimately, such an environment is essential not only for developing self-confidence but also for fostering a healthy personality and identity in the child.
4. C Style (Conscientious and Careful)
Parents with a C style place great importance on order, accuracy, and quality. They usually pay close attention to details and tend to create a structured and organized environment for their children. These characteristics can help the child become responsible and meticulous, gaining self-confidence through completing tasks correctly.
For example, a child raised in an organized environment may learn how to manage their time effectively and accomplish tasks efficiently. This type of upbringing can help the child achieve greater success in their future education and career.
However, if parents are overly critical or perfectionistic, the child may feel that they are never good enough. This perception can lead to decreased self-confidence and anxiety, as the child may constantly strive to meet the high expectations of their parents. In such circumstances, the child might hold back their creativity and initiative, focusing instead on seeking parental approval and validation.
Overall, balance is crucial in this type of parenting. Parents need to balance encouraging order and accuracy with accepting mistakes and failures. This approach can help the child feel secure while also developing the skills necessary to cope with life’s challenges and difficulties.
Ultimately, parents who follow these principles can support the healthy and successful growth of their children while teaching them how to effectively manage life’s pressures and expectations.
Additional Points
Alignment between Parents’ Style and Child’s Personality: It is essential that a parent’s behavioral style aligns with the child’s personality traits to support healthy growth and development. This alignment means that parents need to have a deep understanding of their child’s personality and needs and adjust their parenting methods accordingly.
For example, an energetic child who naturally gravitates toward physical and social activities may feel stifled by an overly strict parent who imposes numerous rules and restrictions. Such a parenting style can make the child feel unable to express themselves and explore the world around them, potentially leading to issues such as anxiety, low self-confidence, or even problematic behaviors.
On the other hand, parents with a more flexible parenting style who pay attention to their child’s emotional and personality needs can create an environment where the child feels safe and free. These parents can encourage their children to engage in creative and social activities, helping them discover their abilities while also establishing healthy boundaries.
As a result, striking an appropriate balance between freedom and limitations can foster the development of a well-rounded and healthy personality in the child. Therefore, understanding and considering a child’s personality traits not only allows parents to optimize their parenting approaches but also gives children the opportunity to grow in a supportive and constructive environment.
Supportive Feedback Instead of Criticism: The type of feedback parents provide has a direct impact on a child’s self-efficacy. Phrases like “I know you tried” or “I believe in your abilities” are far more constructive than “Why couldn’t you do it?” This kind of positive feedback not only helps the child feel valued but also boosts motivation and self-confidence when facing challenges and obstacles.
Specifically, when parents use encouraging language, the child learns that mistakes and failures are a natural part of the learning process and should not lead to discouragement. Additionally, supportive feedback can contribute to the development of the child’s social and emotional skills. When a child feels safe and supported, they are more likely to share their feelings and experiences with their parents, and this closer communication can improve the overall quality of family relationships.
For example, if a child struggles with a homework assignment, and the parents, instead of criticizing, ask what they don’t understand and reassure them that with more effort they can succeed, this approach not only improves academic performance but also teaches the child to seek solutions rather than giving in to frustration in difficult situations.
Ultimately, this type of feedback can have long-term effects on the child’s personality and behavior. Children raised in an environment full of support and encouragement typically develop higher self-confidence in adulthood and can cope with life’s challenges more effectively. Therefore, parents should recognize that the type of feedback they provide can significantly influence the growth and development of their child’s personality.
Parents as Role Models: Children learn more from their parents’ behavior than from any direct instruction. This modeling is not limited to behavioral aspects; it also encompasses attitudes, emotions, and even moral values. When a parent demonstrates healthy self-confidence, the child unconsciously internalizes the same mindset. This process is particularly important during the early years of life when the child’s personality is still developing.
Through their behaviors and reactions to various challenges and situations, parents teach their children how to face problems and successes. For example, if parents remain calm and patient when dealing with life’s difficulties and seek solutions instead of succumbing to despair, the child learns to adopt the same approach and, in similar situations in the future, will look for solutions rather than give in to frustration.
Moreover, parents who believe in themselves and their abilities convey to the child that they too can achieve their goals and move toward success. Additionally, by showing love and support, parents strengthen the child’s sense of worth and security. These positive feelings can help foster an independent and self-confident personality in the child.
Conversely, if parents are constantly critical of themselves or others, the child may develop feelings of inadequacy and low self-esteem. Ultimately, parents serving as role models and their profound influence on children’s personality development highlight the critical importance of parental roles in shaping the upbringing and future of their children.
Practical Recommendations
The results of this analysis indicate that the DISC behavioral model can play an important role in understanding the relationship between parenting styles and children’s self-confidence.
In general, S and I styles, which emphasize emotional support, stability, and positive encouragement, provide the best environment for fostering self-confidence. These styles pay particular attention to the child’s emotional and psychological needs and create a safe and calm space for expressing feelings and thoughts.
In the S style, which is supportive and empathetic, parents or caregivers establish strong emotional connections, conveying to the child a sense of acceptance and love. This type of interaction may include active listening, expressing affection, and encouraging the child to share their feelings and needs.
On the other hand, the I style, which is inspiring and motivational, focuses on encouragement and fostering motivation in the child. Parents or caregivers use positive reinforcement and continuous encouragement to guide the child toward achieving their goals and aspirations. This support can include praising accomplishments, even small ones, and helping the child identify and strengthen their strengths.
In contrast, D and C styles, when applied excessively in terms of control or criticism, may unintentionally undermine a child’s self-confidence. The D style, which is assertive and controlling, may adopt a harsh approach, criticizing the child’s behaviors and choices. This can lead to feelings of insecurity and inadequacy, as the child may feel that they can never meet high expectations.
Similarly, the C style, which is precise and analytical, if applied excessively, can result in constant criticism and inflexibility. Such criticism can affect the child’s self-perception and lead them to doubt their abilities. Consequently, if not balanced, these two styles can have a serious negative impact on the development of the child’s self-confidence and may prevent them from reaching their full potential.
Practical Recommendations for Parents
1. Know Your Behavioral Style: Take the DISC assessment to understand your behavioral strengths and challenges.
2. Celebrate Your Child’s Small Achievements: Emphasizing progress, not just outcomes, reinforces a sense of capability.
3. Allow Mistakes: Children need to learn that failure is a natural part of the growth process.
4. Practice Active Listening: Listening without judgment enhances the child’s sense of self-worth.
5. Trust Your Child: Parental trust acts as a mirror in which the child sees themselves.
Suggested References for Further Reading
Extended DiSC. “How Does Understanding Your DiSC Style Support Your Parenting.” 2021. Extended DISC Blog
PeopleKeys. “Children’s DISC Report + Cognitive.” PeopleKeys
“Different Children Different Needs.” (PDF) – St. Mac Dara's
Beedu, G.K. “A study on the effectiveness of DiSC personality test.” 2021. Selinus University
Assessments24x7. “Kids DISC Assessm




Comments